Asian stock markets have presented an opportunity along with a challenge for investors. The region offers some of the highest economic growth globally and includes large countries with populations that are moving steadily upwards into the middle-class. Also, in terms of relative stock market valuation, the combination of potential dollar weakness and low-price multiples makes Asian markets look attractive compared with other regions. Yet, Asian markets have also been some of the most volatile and difficult for investors to predict, particularly with geopolitical issues but also understanding domestic policies and politics.
How can investors gain access to this region while limiting downside?
Our view is that Asian convertible bonds represent a way to get access to Asian issuers that can broadly replicate overall equity market returns, but with features unique to this market that introduce a good degree of capital preservation and asymmetry of returns, providing participation in markets without having to assume outsized risks.
Attractive Asset Class Features
Convertible bonds possess some features not widely available in other asset classes. Among the most attractive features is that over 80% of Asian convertible bonds have embedded put options, which essentially means that as investors, we can return the bonds at a predetermined price (usually par) back to the company. This feature is very attractive to investors as it reduces the credit spread on the bond, enhancing the risk reward characteristics significantly as the proximity to bond floor remains high which reduces potential downside, yet the upside potential is unaffected. Additionally, Asian convertibles tend to trade cheap in valuation terms when we examine the value of a bond plus its embedded option versus its market value. This cheapness is a structural feature of the Asian convertible bond market and one we feel investors should take advantage of. We notice this cheapness with smaller issues that might fly under the radar of large global funds, or where there are challenges for shorting stocks, which is a trade setup needed for relative value investors to force convertibles closer to their fair price. We think that the benefit of this cheapness further enhances convexity as cheap bonds tend to trade closer to bond floors and closer to parity. This essentially means that if underlying equities were to decline, the proximity to bond floor is high. A high bond floor provides a good level of capital preservation, while conversely if the underlying equity were to rise, participation to the upside would be strong.
Considering both these aspects of Asian convertibles, i.e. capital preservation from bonds with put options that contain structurally inexpensive options, can lead to returns close to those earned from broad stock market exposure, but with substantially less risk. We see this confirmed in the data we have on long term Asia convertible performance, where the level of participation that the asset class has demonstrated when compared to equities is high, with a substantially lower volatility of returns, providing a great way for investors to access the region in a more efficient fashion.
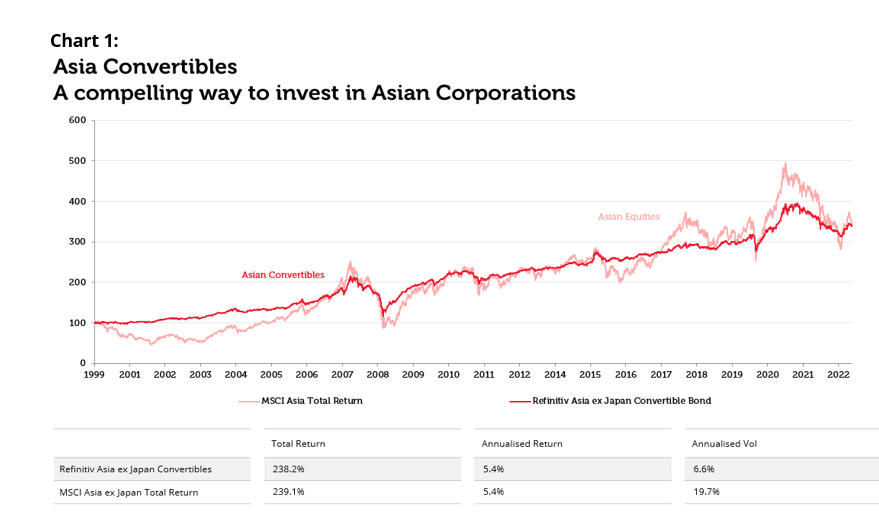
Source: Bloomberg, data range 31st December 1999 to 28th February 2023. Past performance is not a guide to future results. The information shown above is for illustrative purposes.
Universe and Market study
Asian convertible bonds represent approximately $50bn (by market value) and part of a global market totalling approximately $500bn (source: Bloomberg, Refinitiv as at 31st March 2023). Issuers raise capital in this form because of the flexibility that a convertible bond can provide. These reasons might include raising equity-like capital without immediately issuing new shares, coupon savings compared with straight debt, or in the case of an exchangeable bond, allowing a holder of shares to sell them at a premium using their own credit.
We find that the issuers represented in the Asian convertibles market generally offer diversification, with more representation from faster-growing companies. The market itself does constantly change, with a maturity at launch of 5 years on average, which in Asia often comes with a put that can shorten the life of bonds. Chart 3 shows a current comparison of the Asian convertible market with the MSCI Asia Ex Japan stock market index. It is worth noting that our investable universe does not include China A-Share convertibles, which is a growing but less-integrated capital market. We find that we have more than enough choice with China-related issuers that have Hong Kong or US ADR shares into which bonds convert, and who are governed by securities law and regulation more in line with global standards
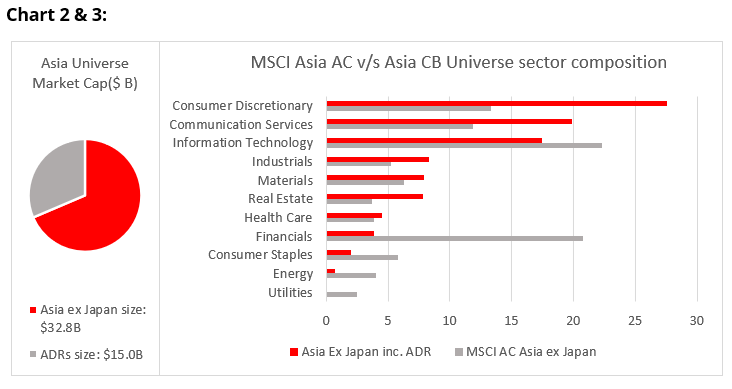
Source: Redwheel, Bloomberg as at 31st March 2023. The information shown above is for illustrative purposes.
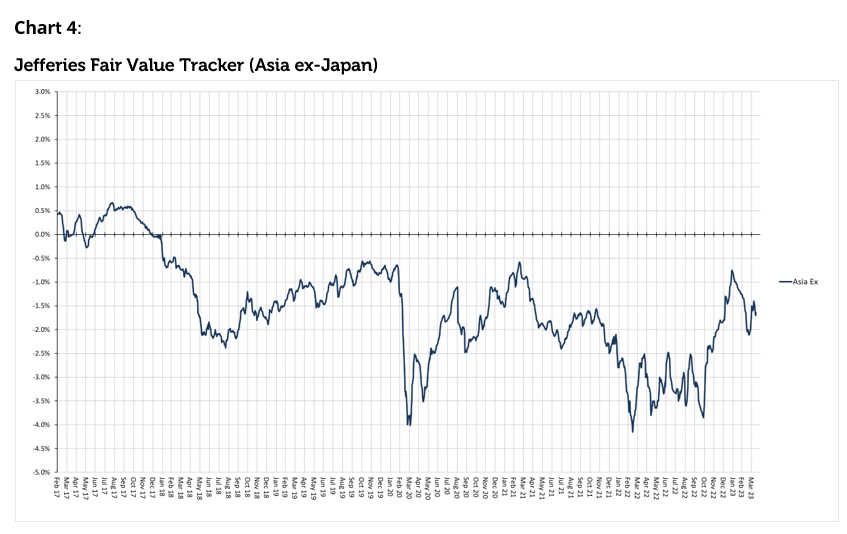
Source: Jefferies, as at 31st March 2023. Past performance is not a guide to future results. The information shown above is for illustrative purposes.
Hynix case study: Heads I win, Tails I get my coupon and principal back.
To illustrate how we believe convertibles are an attractive way to gain equity exposure while limiting risk, we will use an example of a recently issued convertible bond.
Convertible bond investors with a long memory will remember a glut of issuance in the 2010-2015 period from the large players in the memory and storage industry. Micron, Hynix, Western Digital, Sandisk and Nanya all launched convertible bonds to finance expansion and navigate the cyclical downturn of that time. Recently, SK Hynix returned to the primary market with a jumbo $1.7 bn convertible maturing in 2030 (with a put in 4 years) that bears a coupon of 1.75%, a conversion premium of 27.5%, and a formal rating from Moody’s of Baa2.
Since an extended downcycle of 2012, the DRAM market has largely been dominated by an oligopoly where Samsung, Hynix and Micron together hold 95% market share. While there has been consolidation of suppliers, the market has remained cyclical in nature. These companies’ products remain commodity-like in that they are similar in terms of their capabilities and have a sensitivity to cyclical end markets. Now, after a strong upcycle driven by a COVID-led consumption boost, the last 24 months have marked the start of a downcycle which has raised fears of oversupply and slowing down of end markets, leading in part to a retracement that has averaged 30% for these companies. It might be the case that these stocks are undervalued if fears are overblown, but it may also turn out that the damage is worse than expected.
For investors looking to gain exposure to this industry while mitigating some risk from falling stock prices, the recently issued Hynix convertible bond offers an asymmetric way to invest. Hynix currently trades with an equity valuation under 1x P/B value, which has historically proven to be a good entry point. The convertible bond provides investors a long-dated call option on the stock that lasts for seven years, which allows for plenty of time for the industry to recover. Should the equity story not materialise, the put option in 4 years allows investors to get their capital back. (The presence of put options in the convertible bond is a feature unique to the Asian region – over 80% of the convertible bonds in the universe have such an option.) A put enables investors to gain long dated exposure to equity upside with the support of knowing that credit risk is shorter, strengthening the bond floor component of the convertible, and enabling a strong upside/downside capture ratio.
The Redwheel Asia Convertibles Strategy
The philosophy underlying the Redwheel Asia Convertibles Strategy is to try and extract the unique characteristics of the Asia convertibles universe, to allow investors to get exposure to the region in an efficient manner and to extract a benefit from the inherent structural cheapness of the region. We have a long-term 10+ year track record for managing this regionally focused strategy. Our process starts with understanding each issuer from the bottom-up and analysing the investment case. We use our experience with convertible bonds to review structures and identify those that offer an asymmetric payoff along with solid credit fundamentals and support, such as puts. We combine all these aspects in portfolio construction to maximise the ratio of the potential upside from stock returns versus the protection offered by the bond component. Charts 5 and 6 show that since inception, the fund has captured approximately 40% of the equity market performance on average, while capturing just over 25% of the downside, hence giving it an overall upside to downside capture ratio of 1.57x. Our track record since inception shows not only the level of outperformance extracted over our index, but also how well the asset class has performed over equities over the same period, given the strong level of participation with substantially lower volatility of returns.
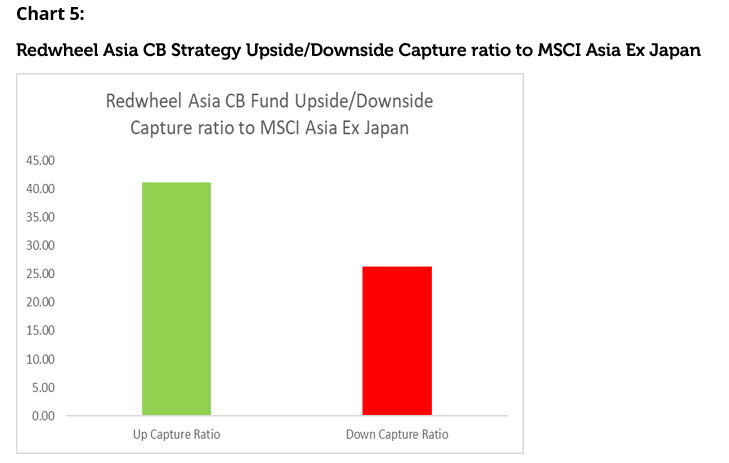
Source: Redwheel, as at 31st March 2023. The information shown above is for illustrative purposes.
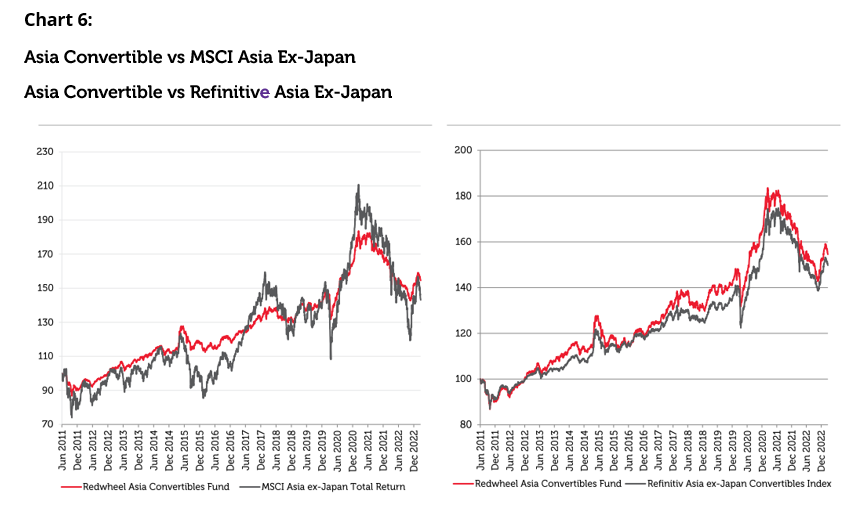
Source: Redwheel, Bloomberg, date range 08 June 2011 to 31 March 2023. Past performance is not a guide to future results. The information shown above is for illustrative purposes.
Key Information
No investment strategy or risk management technique can guarantee returns or eliminate risks in any market environment. Past performance is not a guide to future results. The prices of investments and income from them may fall as well as rise and an investor’s investment is subject to potential loss, in whole or in part. Forecasts and estimates are based upon subjective assumptions about circumstances and events that may not yet have taken place and may never do so. The statements and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author as of the date of publication, and do not necessarily represent the view of Redwheel. This article does not constitute investment advice and the information shown is for illustrative purposes only.

